Organizational Business Communication and Its Major Forms
Organizational business communication is the lifeblood of any enterprise. It influences productivity, fosters teamwork, and drives decisions. Essentially, it forms the framework through which all business activities function. Whether it’s the CEO sending strategic directions or a customer care agent addressing concerns, communication flows must stay clear, purposeful, and efficient. Therefore, understanding the main forms of organizational business communication is essential for every professional.
In today’s fast-paced corporate world, companies must maintain seamless internal and external communication. This ensures not only smooth operations but also strategic development. Let us now dive deep into its two broad categories: internal communication and external communication, followed by detailed insights into the channels they utilize.
What is a Communication Flow?
Before exploring its types, one must understand the meaning of communication flow. A communication flow refers to the direction in which information travels within or outside the organization. Depending on organizational structure, hierarchy, and function, this flow can move downward, upward, horizontally, or externally. Moreover, communication flow isn’t just about message movement — it includes clarity, speed, feedback, and purpose.
Thus, to ensure effective organizational business communication, firms must actively shape their communication channels based on their goals.
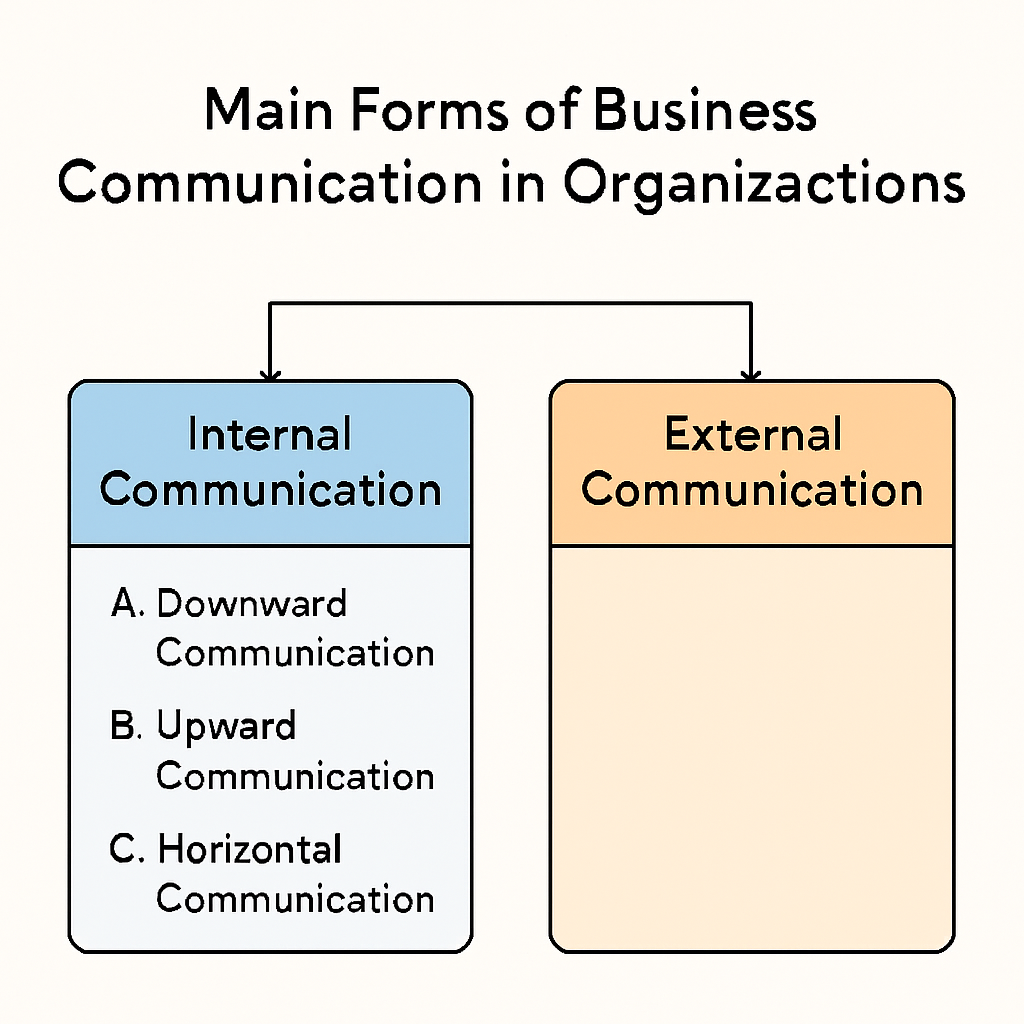
1. Internal Communication
Internal communication refers to the exchange of messages and information within the organization. It helps employees understand their roles, responsibilities, and expectations. Furthermore, it fosters a sense of unity and shared purpose among the workforce. When this communication is strong, the entire organization benefits.
It is divided into three core subtypes:
➤ A. Downward Communication
Downward communication flows from the top-level management to lower-level employees. It is used by managers and supervisors to deliver important instructions. Additionally, it includes job assignments, policy announcements, and performance feedback.
Moreover, it sets the tone for operations. For example, if a CEO introduces a new vision or policy, it must be communicated to all staff accurately. This channel also informs employees about expectations, responsibilities, benefits, and disciplinary actions.
Common tools for downward communication include:
- Official memos
- E-mails from executives
- Policy manuals
- Staff meetings
- Newsletters
Benefits of downward communication:
- Ensures discipline and structure
- Clarifies employee roles
- Builds organizational unity
- Reduces uncertainty during crises
However, without clarity and respect, it may lead to misunderstandings or resentment. Therefore, downward communication must remain concise and respectful.
➤ B. Upward Communication
Upward communication flows from subordinates to higher management. It helps employees share feedback, complaints, ideas, and concerns. Hence, it acts as a mirror, reflecting the effectiveness of policies and management practices.
Without upward communication, senior management operates in the dark. Consequently, decisions may become disconnected from ground realities. Encouraging upward communication builds trust and improves morale.
Examples of upward communication include:
- Staff feedback forms
- Suggestion boxes
- Employee performance reports
- One-on-one meetings with managers
- Open-door policy interactions
Benefits of upward communication:
- Encourages participation
- Highlights issues early
- Inspires innovation
- Improves problem-solving
Still, this form of communication demands a culture of openness. Otherwise, employees may feel hesitant to share honestly.
➤ C. Horizontal Communication
Also known as lateral communication, this channel operates between departments or employees of equal rank. For instance, the marketing team collaborating with the sales department, or the HR head discussing policies with the finance manager.
Its purpose is to coordinate efforts, share insights, and resolve inter-departmental problems. It becomes especially vital during joint projects or deadlines. Moreover, horizontal communication enhances efficiency by avoiding duplication of efforts.
Tools used in horizontal communication:
- Team collaboration apps (like Slack or Teams)
- Inter-department meetings
- Brainstorming sessions
- Informal discussions
Benefits of horizontal communication:
- Promotes teamwork
- Solves problems faster
- Enhances innovation
- Reduces misunderstandings
That said, this form can sometimes cause conflict if not managed properly. Hence, a spirit of cooperation must guide it at all times.
2. External Communication
External communication refers to interactions between the organization and external parties. These can be customers, suppliers, investors, government bodies, media houses, and the general public. Such communication shapes the company’s image, builds trust, and supports growth.
Without proper external communication, even a great product can fail. Companies must remain transparent, responsive, and professional in all external messaging. After all, public perception often defines success.
➤ A. Communication with Customers
This is the most vital form of external communication. Businesses survive by meeting customer needs. Therefore, communication channels like customer service, email support, chatbots, and advertising must always stay strong and aligned.
Customer communication includes:
- Answering queries
- Handling complaints
- Promoting new products
- Gathering feedback
➤ B. Communication with Suppliers and Vendors
Suppliers are essential business partners. Clear communication regarding pricing, delivery, quality, and timelines prevents disruptions. Any miscommunication can lead to delays or losses.
Key elements include:
- Purchase orders
- Contracts
- Inventory updates
- Dispute resolution messages
➤ C. Communication with Government and Regulators
To remain legally compliant, firms must constantly communicate with regulatory bodies. Filing taxes, renewing licenses, or reporting environmental data all require formal communication.
➤ D. Communication with Media and Investors
Public relations departments handle media releases and investor relations. Their communication maintains brand reputation, boosts investor confidence, and clarifies the company’s vision.
Channels used:
- Press releases
- Investor briefings
- Financial reports
- Public speeches
➤ E. Communication with Competitors and Collaborators
Even competitors communicate, especially when industries join forces to lobby or create joint ventures. Maintaining ethical and legal communication in such cases is key.
Importance of Communication Channels
So, what exactly are communication channels? Simply put, a communication channel is the medium used to transmit a message. In the workplace, the choice of channel can make or break the message’s effectiveness.
➤ Formal Channels
Formal channels follow the official hierarchy. These are structured, documented, and traceable. Such channels reduce ambiguity and enhance professionalism.
Examples include:
- Memos
- Official letters
- Scheduled meetings
- Project management tools
➤ Informal Channels
Also called the grapevine, these channels are unofficial. They include casual conversations and hallway discussions. Although informal, they spread news quickly and often influence morale.
However, organizations must monitor informal communication to avoid gossip or misinformation.
Digital Communication in Modern Businesses
In today’s digital world, technology-driven communication has become the norm. Whether internal or external, most messages are now sent digitally.
➤ Email Communication
Email remains the backbone of corporate messaging. It allows for detailed, recordable, and timely interactions.
➤ Instant Messaging Tools
Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and WhatsApp help with fast, casual communication.
➤ Video Conferencing
Tools like Zoom and Google Meet enable remote meetings. Especially after COVID-19, this form became indispensable.
➤ Social Media
Externally, companies use platforms like Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook to engage with audiences, manage reputation, and announce updates.
➤ CRM and ERP Systems
Businesses also rely on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to automate communication and ensure consistency.
Role of Communication in Business Success
Now that we understand the organizational business communication forms, let us explore their broader impact.
➤ Enhances Decision Making
Proper communication ensures that everyone has access to relevant information. As a result, decisions become timely, informed, and goal-driven.
➤ Builds Employee Morale
When employees feel heard, they stay motivated. Therefore, upward and horizontal communication directly boosts morale and loyalty.
➤ Improves Efficiency
Clear instructions save time. Moreover, coordinated teams reduce overlaps and errors, boosting overall productivity.
➤ Strengthens Customer Relations
A company that communicates transparently with its customers earns loyalty. Additionally, quick response times enhance trust and satisfaction.
➤ Encourages Innovation
Horizontal and upward channels allow the free flow of ideas. Creative employees thus get a platform to express and contribute.
Challenges in Organizational Business Communication
Despite its importance, communication in businesses can face several obstacles.
➤ Information Overload
Too many messages can overwhelm employees, causing them to miss important updates.
➤ Miscommunication
Lack of clarity or incorrect assumptions may lead to costly errors.
➤ Technological Barriers
Not everyone is tech-savvy. Moreover, technical issues can hinder timely communication.
➤ Cultural and Language Differences
In global organizations, cross-cultural communication requires sensitivity and training.
➤ Noise and Distractions
Disruptions or multitasking can dilute the effectiveness of communication.
Tips for Effective Communication
To ensure that organizational business communication remains impactful, follow these principles:
- Be clear and concise
- Choose the right channel
- Encourage feedback
- Avoid jargon
- Be respectful and empathetic
- Use visuals where needed
- Train employees in communication tools
- Keep communication timely and relevant
Conclusion
In conclusion, organizational business communication is essential for any company’s success. Whether it’s downward instructions, upward feedback, or cross-department discussions, each flow plays a unique role. Externally, strong communication ensures customer satisfaction, legal compliance, and brand loyalty.
Furthermore, in a digital age, communication channels are evolving fast. Businesses must embrace new tools, encourage open dialogue, and train their teams accordingly. Only then can they ensure smooth operations, strong relationships, and long-term growth.
By mastering internal and external communication flows, businesses don’t just survive—they thrive. Thus, it is no exaggeration to say that clear communication is the heart of every successful enterprise.
Communication and Its Importance in Modern Business: https://englishwithnaeemullahbutt.com/2025/08/07/importance-of-business-communication/
Visit Google to search for English literature topics, authors, and study resources:https://www.google.com
Discover more from Naeem Ullah Butt - Mr. Blogger
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
